- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Home
- Low Back Pain TreatmentsNeck & Shoulder Pain TreatmentsLeg & Foot Pain Treatments
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
Contents
Toggle- Creating an individualised treatment plan
- The role of different specialities (physiotherapist, orthopaedist, psychologist, neurosurgeon)
- Pain treatment during pregnancy
- Treatment of chronic pain in the elderly
- Pain management in children
- Stress management
- Healthy eating
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Exercise and mobility
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Cancer pain
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port Application
- Vascular Port (Permanent Vascular Access)
- Trigeminal Nerve RFT
- Blockade of Ganglion Stellatum
- Lumbar Sympathetic Ablation
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Hernia Burning (IDET)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port - Pump System
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Peripheral Nerve Block
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Intra-articular Fluid Treatment
- Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Nucleoplasty
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Herbal solutions
- Dry needle treatment
- Anti-ageing treatments
- Ozone therapy
- Cupping therapy - Cupping
- Mesotherapy
- Prolotherapy
- Acupuncture
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Nerve blockages
- Corticosteroid injections
- Massage and relaxation techniques
- Manual therapy
- Electrotherapy
- Neuropathic pain medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Muscle relaxants
- Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)
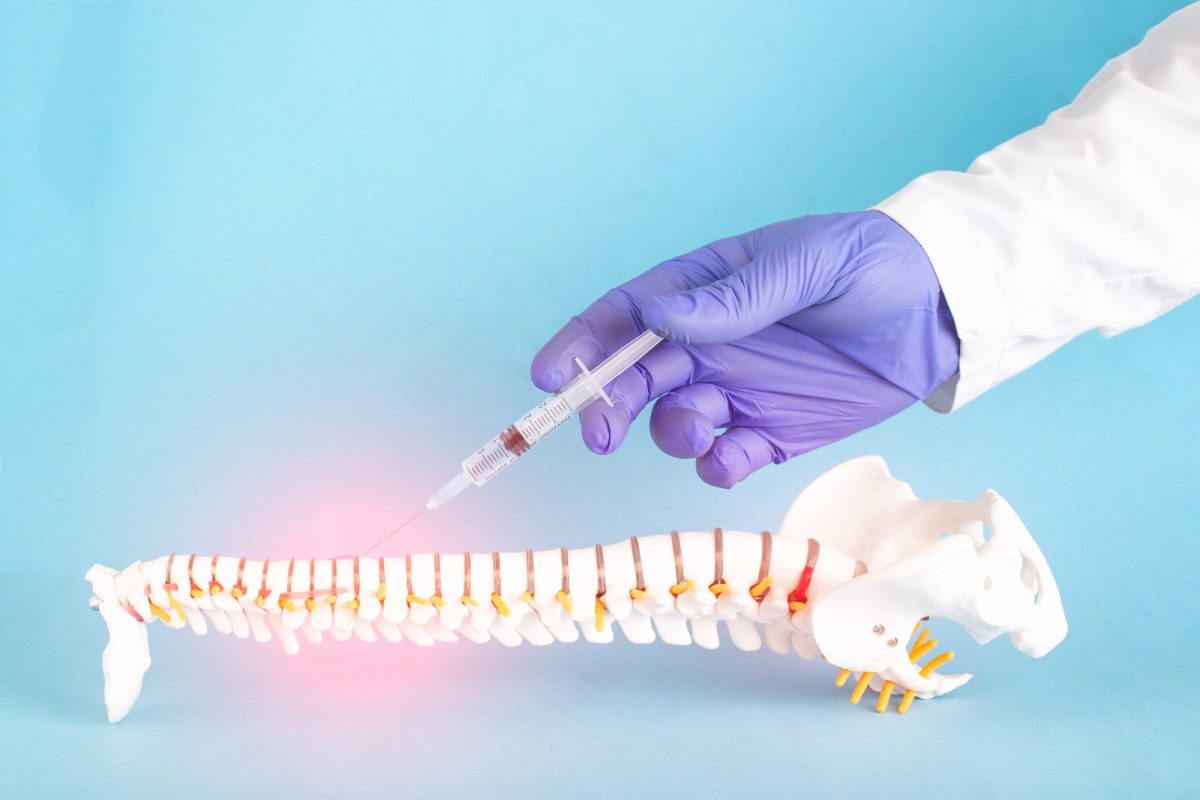
Transforaminal epidural injectionis a minimally invasive treatment method, also known colloquially as "pinpoint injection", which involves the direct administration of medication to the area where the nerve roots are located in the spine (foramen). This procedure is often used to control pain caused by conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis or nerve inflammation that compress the nerve roots. The treatment is called "pinpoint" because it targets a specific nerve root with high precision.
What is Transforaminal Injection?
- What is a Foramen? They are small openings between the bones of the spine through which the nerve roots pass. The nerves coming out of these openings provide sensation and movement to certain parts of the body.
- Procedure: In a transforaminal injection, the drug is injected directly into this opening and around the nerve root. The medication usually contains an anti-inflammatory corticosteroid and a local anaesthetic.
In which cases is it used?
- Herniated Disc (Herniation):
- To relieve the pain caused by herniated discs pressing on the nerve root.
- Sciatica Pain (Radiculopathy):
- In pain caused by pressure on the nerve root and radiating to the leg.
- Spinal Stenosis
- In cases where the nerve roots are compressed as a result of narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS):
- In the management of chronic nerve pain.
- Nerve Inflammation:
- In pain caused by inflammation of the nerve root (radiculitis).
- Postoperative Pain:
- Postoperative pain in the nerve roots.
How is the Procedure Performed?
1. Preparation:
- The patient is evaluated before the procedure and the nerve root that is the source of the pain is determined by imaging (MR, CT).
- The procedure is usually performed under local anaesthesia. Light sedation can be applied when necessary.
2. Patient Position:
- The patient is positioned in prone or side lying position.
- The target area is sterilised.
3. Imaging Assisted Needle Placement:
- Using fluoroscopy (X-ray guidance) or ultrasound, the needle is guided into the foramen where the nerve root is located.
- Contrast medium may be injected to make sure the needle is in the correct position.
4. Drug Administration:
- The medicine is carefully injected around the nerve root.
- The injected drug reduces inflammation and relieves pressure on the nerve.
5. Completion:
- The procedure usually takes 20-30 minutes.
- After the needle is removed, the area is sterilised and the patient is kept under observation for a short time.
Advantages
- Targeted Treatment: Since the drug is delivered directly to the nerve root that is the source of the pain, it provides a more effective result.
- Minimally Invasive It is applied without the need for surgical intervention.
- Fast Recovery: After the procedure, the patient can usually return to normal activities on the same day.
- Reduces Pain Fast: Provides pain control in a short time by reducing inflammation.
- Compliance with Physical Therapy: The reduction of pain allows the patient to adapt to physical therapy more easily.
Who is it suitable for?
- Patients with leg or arm pain caused by a herniated disc.
- Individuals with restricted mobility due to spinal canal narrowing or nerve compression.
- Chronic pain patients who do not respond to other treatments (medication, physiotherapy).
- People who are not suitable for surgical intervention or who do not prefer surgery.
Risks and Side Effects
Transforaminal injection is usually a safe procedure, but the following risks may rarely occur:
- Infection: Infection may occur in the treated area.
- Nerve Injury The risk of nerve damage is very low in the procedure performed close to the nerve root.
- Haemorrhage The risk may increase in patients taking blood thinners.
- Temporary Side Effects: Temporary numbness, weakness or tenderness at the injection site may occur.
- Steroid Side Effects: Temporary effects such as flushing, insomnia, increased blood sugar.
Post Procedure Care
- Rest After the procedure, the patient should rest for several hours.
- Light Activities: Heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided on the first day.
- Impact: The effect of corticosteroids is usually felt within a few days and can reduce pain for 6-12 months.
- Doctor's Check-up: If new symptoms (severe pain, signs of infection) occur, consult a doctor.
Success Rate
- Transforaminal enjeksiyon, doğru hasta seçimi yapıldığında %70-90 oranında etkili bir tedavi yöntemidir.
- The duration of action varies from individual to individual and usually provides pain relief for several months to a year.
Conclusion
Transforaminal epidural injection (pinpoint), It is a safe method to treat nerve root pain originating from the waist and neck effectively and quickly. Thanks to its minimally invasive nature, patients can achieve relief without the need for surgery. However, the appropriateness and success rate of this treatment should be evaluated by a specialist physician depending on the source of the pain and the general health status of the patient.
Our treatments
- Home
- Low Back Pain TreatmentsNeck & Shoulder Pain TreatmentsLeg & Foot Pain Treatments
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)