- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)
- Home
- Medication Therapy
- Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)
Contents
Toggle- Creating an individualised treatment plan
- The role of different specialities (physiotherapist, orthopaedist, psychologist, neurosurgeon)
- Pain treatment during pregnancy
- Treatment of chronic pain in the elderly
- Pain management in children
- Stress management
- Healthy eating
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Exercise and mobility
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Cancer pain
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port Application
- Vascular Port (Permanent Vascular Access)
- Trigeminal Nerve RFT
- Blockade of Ganglion Stellatum
- Lumbar Sympathetic Ablation
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Hernia Burning (IDET)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port - Pump System
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Peripheral Nerve Block
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Intra-articular Fluid Treatment
- Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Nucleoplasty
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Herbal solutions
- Dry needle treatment
- Anti-ageing treatments
- Ozone therapy
- Cupping therapy - Cupping
- Mesotherapy
- Prolotherapy
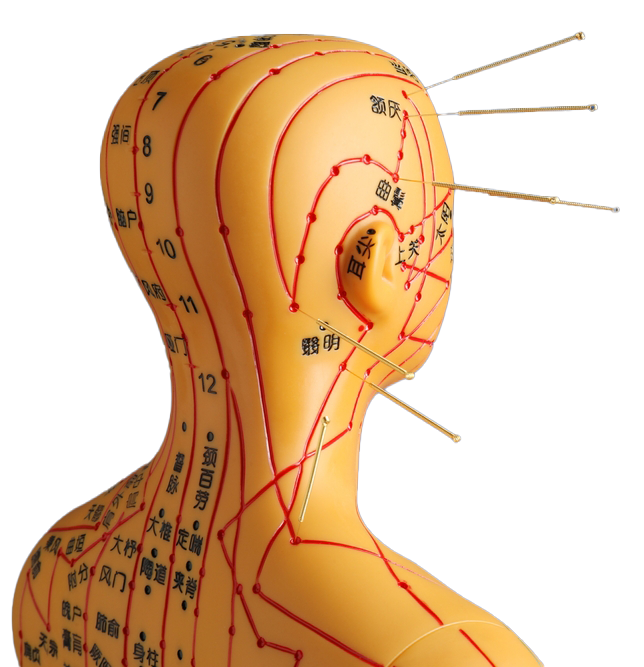
- Acupuncture
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Nerve blockages
- Corticosteroid injections
- Massage and relaxation techniques
- Manual therapy
- Electrotherapy
- Neuropathic pain medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Muscle relaxants
- Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)
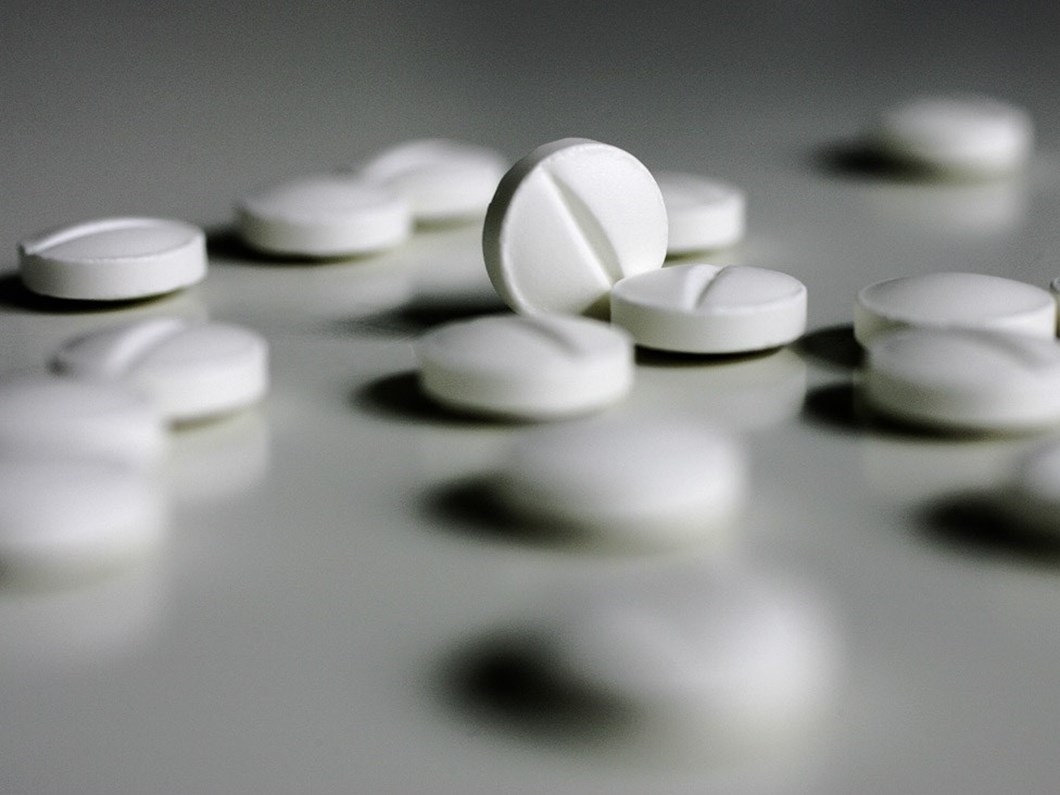
Painkillers: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and More
Pain is our body's way of telling us that something is wrong. It often reduces the quality of our daily life; it can negatively affect many things, from working to the activities we enjoy. One of the most common methods of dealing with pain is painkillersis. In this article, we will examine what common painkillers, especially paracetamol and ibuprofen, do, how they should be used and their possible side effects.
What are Painkillers and How Do They Work?
Painkillers (analgesics) are designed to stop or reduce the processes in the body that trigger or maintain pain. They prevent pain signals from reaching the brain or control the body's inflammatory processes.
For example:
- Paracetamol (Acetaminophen): Reduces the effect of pain signals reaching the brain by increasing the pain threshold.
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) such as Ibuprofen, Naproxen: It reduces pain, fever and inflammation by inhibiting the production of substances called prostaglandins that trigger the body's inflammatory process.
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
How does it work?
Paracetamol helps to relieve the perception of pain in your nervous system and reduces fever. However, its anti-inflammatory effect is not very strong. It is often preferred especially in mild to moderate pain such as headache, toothache and fever.
Dosing and Handling
- In adults it is usually used as a tablet in the form of 500 mg or 1000 mg.
- It is usually a rule of thumb not to exceed 4 grams (4000 mg) per day, as high doses can damage the liver.
- For children, a special dose should be adjusted according to age and weight.
Things to Consider
- Overdose can seriously impair liver function.
- If you have chronic liver disease or drink alcohol regularly, you should not take paracetamol without consulting your doctor.
- Long-term use without a doctor's recommendation may increase the risk of liver damage.
Ibuprofen and Other NSAIDs
How does it work?
Medicines in the NSAID group, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, work by reducing both pain and inflammation. For example, if you have arthritis in your knee or tension that causes a headache, these medicines often provide relief.
Dosing and Handling
- Ibuprofen is usually available over-the-counter in adults in 200-400 mg doses. Higher doses may require a doctor's prescription.
- How much you can take per day depends on your age, health condition and the severity of your pain. Your doctor or pharmacist can recommend a special programme for you.
Things to Consider
- Long-term use of high doses of NSAIDs can cause irritation of the stomach and intestines, even ulcers and bleeding.
- Those with a history of stomach upset, gastritis or ulcers should take NSAIDs under the supervision of a doctor.
- NSAIDs may also pose a risk for people with a history of heart disease and high blood pressure. It is therefore important to seek medical advice.
Which painkiller should be preferred when?
- Mild pain and fever (headache, toothache, mild joint pain): Paracetamol can often be the first choice. It causes relatively little damage to the stomach and is safe if you do not have liver problems.
- Inflammatory conditions (arthritis, rheumatism, sports injuries): Ibuprofen or other NSAIDs may be more effective. Because these medicines reduce inflammation and relieve swelling and pain.
- Chronic pain (arthritis, low back pain): Your doctor may recommend NSAIDs or different combinations of medicines. Long-term use should always be followed up by a doctor.
Side Effects and Precautions
- Gastrointestinal Problems: It is especially common in the use of NSAIDs. The risk of stomach pain, heartburn, indigestion and even ulcers and bleeding should be taken into consideration.
- Liver Damage: Paracetamol has a harmful effect on the liver in high doses.
- Kidney Problems: Long-term use of NSAIDs may also put a strain on the kidneys.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, if you experience symptoms such as skin rash or shortness of breath, stop taking the medicine and seek medical advice immediately.
- Interactions: Always consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any medication regularly, as they may interact with other medicines such as blood thinners, blood pressure medicines, diabetes medicines.
Important Points to Consider
- Be Careful Even If Purchased Without Prescription: Paracetamol and ibuprofen are available in pharmacies without a prescription, but they are not "harmless". Label and package leaflet instructions must be followed.
- Do not exceed the daily dose: Taking more than the recommended doses to "get better faster" will do more harm than good.
- Consult a doctor in case of prolonged pain: In pain that lasts longer than a few days or recurs frequently, the use of medication may hide the problem instead of solving it. A medical examination for the underlying cause may be required.
Conclusion
Painkillers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen can be very effective in relieving pain that interferes with daily life or disturbs your comfort. However, unconscious use of these medicines can lead to serious side effects and health problems. It is always safest to consult a doctor or pharmacist to choose the right medication according to the type and severity of the pain and your personal health history.
Remember
Painkillers suppress pain temporarily; they do not eliminate the actual cause of the pain. If you have chronic or recurrent pain, try to determine the underlying cause by getting a specialist opinion and try appropriate treatment methods for a permanent solution.
Our treatments
- Home
- Medication Therapy
- Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)