- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
Nucleoplasty
- Home
- Advanced Treatments
- Nucleoplasty
Contents
Toggle- Creating an individualised treatment plan
- The role of different specialities (physiotherapist, orthopaedist, psychologist, neurosurgeon)
- Pain treatment during pregnancy
- Treatment of chronic pain in the elderly
- Pain management in children
- Stress management
- Healthy eating
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Exercise and mobility
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Cancer pain
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port Application
- Vascular Port (Permanent Vascular Access)
- Trigeminal Nerve RFT
- Blockade of Ganglion Stellatum
- Lumbar Sympathetic Ablation
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Hernia Burning (IDET)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port - Pump System
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Peripheral Nerve Block
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Intra-articular Fluid Treatment
- Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
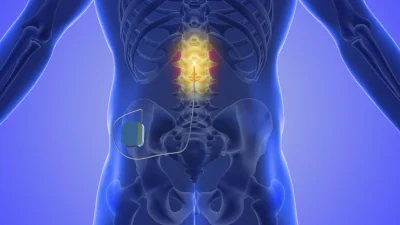
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Nucleoplasty
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Herbal solutions
- Dry needle treatment
- Anti-ageing treatments
- Ozone therapy
- Cupping therapy - Cupping
- Mesotherapy
- Prolotherapy
- Acupuncture
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Nerve blockages
- Corticosteroid injections
- Massage and relaxation techniques
- Manual therapy
- Electrotherapy
- Neuropathic pain medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Muscle relaxants
- Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)
.
Nucleoplasty A Minimally Invasive Approach to Lumbar and Cervical Hernias
Today, spinal disc problems such as lumbar and cervical disc herniations can seriously affect the quality of daily life of many people. Non-surgical or minimally invasive methods are becoming increasingly important for these conditions, which are characterised by pain, numbness and restricted movement. Nucleoplastynucleoplasty stands out as a relatively new and minimally invasive method applied in the treatment of herniated discs. In this article, you can find out what you wonder about nucleoplasty and examine the advantages and processes of this treatment more closely.
1. What is Nucleoplasty?
Nucleoplasty lumbar or cervical hernia is a procedure that uses radio waves and special needles to shrink herniated or damaged areas of the spinal discs. The main aim is to relieve pressure on the nerve roots by reducing the protruding disc material due to degeneration or herniation inside the spine.
How does it work?
- Disc Access: With the help of a guide needle, radio waves or plasma energy is applied to the spinal disc in a controlled manner.
- Reduction of Disc Material: This energy reduces the disc pressure by evaporating or shrinking the excess tissue in the disc.
- Pain Relief: As the pressure inside the disc decreases, the pressure on the nerve root is relieved and pain and numbness symptoms improve.
2. In which cases is it preferred?
- Lumbar and Neck Hernias: It is especially effective in cases where the disc herniation is not completely ruptured, but protrudes enough to compress the nerves.
- Chronic Disc Pains: It can be preferred in disc problems that do not respond to traditional treatments (physical therapy, medication, injection, etc.) but do not require full surgical intervention.
- Moderate Disc Degeneration: It may be a good option in patients in whom surgery would pose a great risk or in patients in whom the hernia is not yet at an advanced stage.
3. How Does the Nucleoplasty Process Work?
- Evaluation and Planning:
- The patient is first evaluated by clinical examination, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT).
- The size of the hernia, disc structure and general health status are examined and a decision on the suitability for nucleoplasty is made.
- Process Preparation:
- The procedure can usually be performed under local anaesthesia or light sedation.
- The patient is positioned on the operating table in a supine or prone position (the position may vary depending on the area to be treated).
- Implementation Phase:
- Using fluoroscopy (live X-ray imaging), a special needle is inserted into the centre of the disc space.
- The device that generates radiofrequency or plasma energy is then switched on. This energy partially vaporises or reduces the disc material.
- This reduces the disc volume and relieves the pressure on the nerves.
- Follow-up and Recovery:
- Nucleoplasty is a short procedure that usually takes between 30-60 minutes.
- The patient is kept under observation for a while after the procedure and can usually return home on the same day.
- The doctor may recommend mild activity restriction during the recovery period, painkillers or muscle relaxants if necessary, and physiotherapy.
4. What are the Advantages?
- Minimally Invasive Approach: It is performed without large incisions and long recovery times, allowing the patient to return to daily life quickly.
- Low Risk of Complications: Compared to conventional surgery, risks such as bleeding, infection or tissue damage are much lower.
- Fast Recovery: Patients can usually start light daily activities shortly after the procedure. It takes a few weeks for them to fully return to their normal routine.
- Chance of Permanent Relaxation: When the appropriate patient is selected, the compression on the nerve is significantly eliminated and a significant reduction in pain can be achieved.
5. Possible Side Effects and Cautions
- Temporary Pain or Discomfort: In the first days after the procedure, soreness or mild pain may be observed at the injection site.
- Risk of Infection: As with any invasive procedure, there is a risk of infection if sterile conditions are not observed.
- Inadequate Response or Need for Repetition: The success rate may be different for each patient. Some patients may not benefit fully from nucleoplasty or may require a similar procedure again in the future.
- Nerve Damage (Rare): There is a very small chance of nerve damage.
Important Notice: Patients with bleeding disorders, active infections and patients with severe disc degeneration or rupture (sequestration) may not be suitable candidates for nucleoplasty.
6. Recommendations for the recovery process
- Physical Therapy and Exercises: It is important to strengthen the muscles and reduce the load on the spine with gentle exercises recommended by the doctor or physiotherapist.
- Correct Posture and Ergonomics: Gaining posture habits that support proper sitting, waist and neck health while working at a desk helps prevent hernia formation or recurrence.
- Weight Control: Excess weight increases the risk of hernia by placing additional load on the spine. A balanced diet and regular exercise to control weight are beneficial in this process.
- Regular Doctor Checks: If the pain returns or worsens, it may be necessary to contact your doctor for further evaluation.
7. Conclusion
Nucleoplasty is a treatment option that is less invasive than surgery and offers rapid recovery for people suffering from spinal disc problems such as herniated discs. Especially if the size of the hernia is at a stage that does not require full surgical intervention and the response to conventional treatments (medication, physiotherapy, etc.) is not sufficient, nucleoplasty may be considered as an effective and safe alternative.
Her ne kadar avantajlı bir yöntem olsa da, nükleoplasti herkese uygun olmayabilir ve her vakada %100 çözüm vaat etmez. Kişisel sağlık durumunuzu değerlendirerek bu tedavinin size uygun olup olmadığını anlamak için bir beyin ve sinir cerrahisi uzmanına ya da fizik tedavi ve rehabilitasyon doktoruna danışmanızda fayda vardır. Sağlıklı bir omurga ve ağrısız bir yaşam için doğru tedaviyi, doğru zamanda, alanında uzman hekimle birlikte seçmek en önemli adımdır. Formun Altı
Our treatments
- Home
- Advanced Treatments
- Nucleoplasty