- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
Electrotherapy
- Home
- Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
- Electrotherapy
Contents
Toggle- Creating an individualised treatment plan
- The role of different specialities (physiotherapist, orthopaedist, psychologist, neurosurgeon)
- Pain treatment during pregnancy
- Treatment of chronic pain in the elderly
- Pain management in children
- Stress management
- Healthy eating
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Exercise and mobility
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Cancer pain
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port Application
- Vascular Port (Permanent Vascular Access)
- Trigeminal Nerve RFT
- Blockade of Ganglion Stellatum
- Lumbar Sympathetic Ablation
- Facet joint Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation (RFT) Treatment
- Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Hernia Burning (IDET)
- Discitis Procedure
- Sacroiliac Joint Radiofrequency Treatment (Simplicity)
- Permanent Epidural / Spinal Port - Pump System
- In-Disc Ozone Therapy
- Nucleoplasty
- Peripheral Nerve Block
- Transforaminal Injection (Pinpoint)
- Facet joint block
- Epidural Injection
- Intra-articular Fluid Treatment
- Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFT)
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Ergonomic living arrangements
- Spinal cord stimulation (pain pacemaker)
- Nucleoplasty
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Herbal solutions
- Dry needle treatment
- Anti-ageing treatments
- Ozone therapy
- Cupping therapy - Cupping
- Mesotherapy
- Prolotherapy
- Acupuncture
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Nerve blockages
- Corticosteroid injections
- Massage and relaxation techniques
- Manual therapy
- Electrotherapy
- Neuropathic pain medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Muscle relaxants
- Painkillers (paracetamol, ibuprofen, etc.)
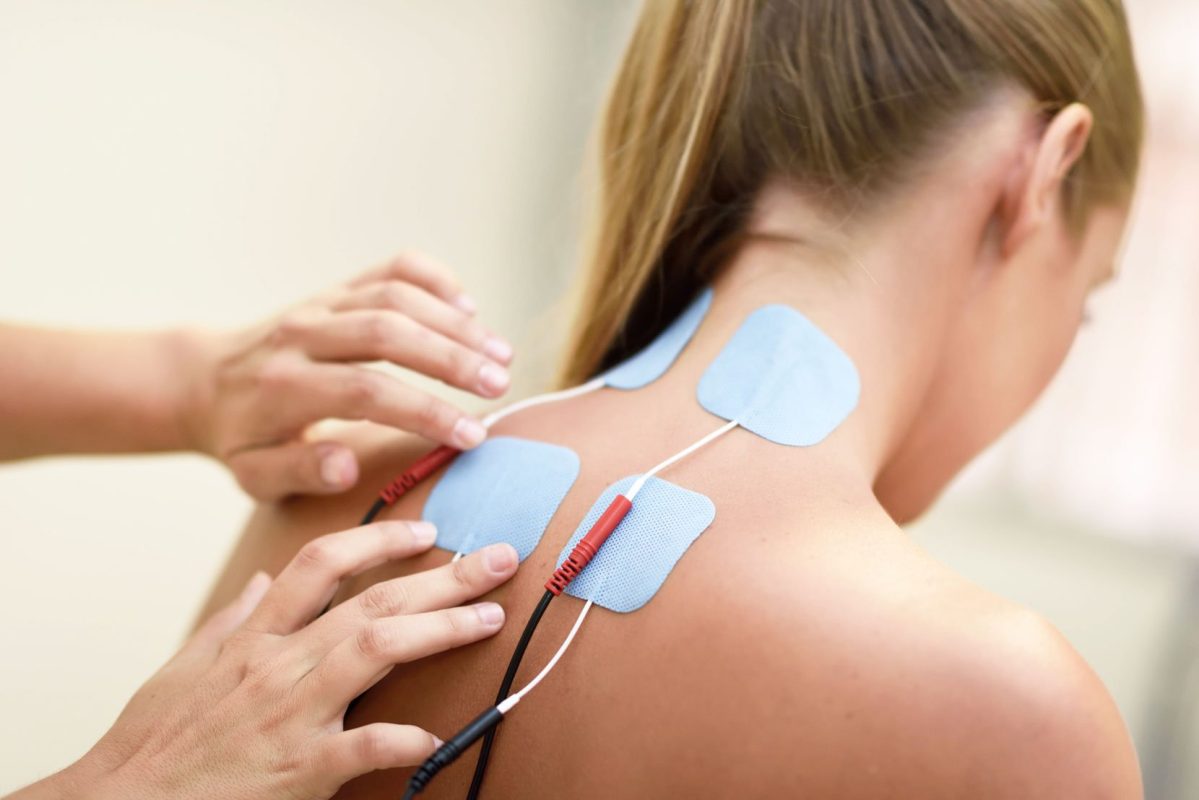
Electrotherapy The Healing Power of Electric Current
Various treatment methods are used to alleviate the body's problems such as pain, muscle weakness or joint movement limitation. One of these is electrotherapyis. Electrotherapy, which is based on the application of electric current to the body at certain intervals and in certain doses, is an effective method that the world of physiotherapy and rehabilitation has been using for a long time. In this article, we will examine how electrotherapy works, in which cases it is used and its benefits.
What is Electrotherapy?
Electrotherapy is a treatment approach that aims to achieve goals such as pain control, muscle strengthening and circulatory improvement by applying low-level electrical currents or waves to specific tissues. Various therapy protocols can be created using different types of currents (TENS, EMS, IFC, etc.). Each current stimulates the body through a different mechanism and provides special results.
Working Mechanism of Electrotherapy
- Nerve Stimulation: Electric waves can temporarily block the pathways that carry pain signals in the nervous system or alter the sensation of pain that reaches the brain. This effect is based on the principle known as "Gate Control Theory".
- Improving Muscle Contractions: Electric current can stimulate muscle fibres to produce contractions. In this way, weakened muscles can be strengthened or muscles that are immobilised after injury can be reactivated.
- Improving Blood Circulation: Electrical stimulation can stimulate blood flow in the treated area and accelerate the nourishment of tissues and the healing process.
Types of Electrotherapy
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation):
It is especially effective in pain control. Low-frequency electrical signals are transmitted to the nerves through the skin to block pain signals. - EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation):
It is used for recovery after muscle weakness or injury. The electric current causes the muscles to contract and relax repetitively, increasing muscle strength and endurance. - IFC (Interference Currents):
It is created by the intersection of two alternating currents with close frequencies inside the body. It contributes to pain control and circulation increase; it can affect deep tissues. - Ultrasound Therapy (can be considered a part of electrotherapy):
Technically, high frequency sound waves are used instead of electric current, but it is often referred to as electrotherapy in physiotherapy protocols. It is effective in deep tissue heating and accelerating healing.
In which cases is it preferred?
- Musculoskeletal System Problems: Muscle tears, muscle weakness, tendonitis, lumbar and cervical hernias.
- Pain Management: Electrotherapy is frequently used in long-term pain syndromes such as chronic low back pain, neck pain, arthritis pain, neuropathic pain.
- Rehabilitation After Surgery: For muscle strengthening and pain management after surgical interventions such as joint replacement operations or meniscus operations.
- Sports Injuries: To support tissue healing after muscle strains, sprains, ligament injuries.
- Circulatory Disorders: It helps to control oedema and pain by increasing blood circulation in the hands and feet.
How does the treatment process proceed?
- Evaluation and Planning: The physiotherapist or specialist doctor examines the patient's complaints, pain level and physical condition. The appropriate method and current type are selected for electrotherapy.
- Implementation: Low-dose electric current is applied with the help of electrodes placed on the skin. Although the frequency of treatment and the length of the session varies according to the needs of the patient, it is usually planned as several sessions per week.
- Follow-up and Progress Evaluation: The patient is monitored during each session and the rate of pain reduction, muscle function and range of motion are observed. Depending on the rate of improvement, the treatment process is adjusted or combined with different types of therapy.
Benefits and Advantages
- Non-drug Pain Control: Especially applications such as TENS can reduce the need for analgesic drugs.
- Fast Recovery: It improves the nutrition of tissues by increasing blood flow and can accelerate the repair of wounds and injuries.
- Increased Muscle Strength: It re-strengthens the muscles weakened as a result of prolonged inactivity or injury.
- Combined Treatment Possibility: More comprehensive results can be obtained by using methods such as exercise, massage, hot-cold applications or manual therapy.
- Minimal Risk of Side Effects: The risk of serious side effects is low with the correct dose and application.
Things to Consider
- Expert Control Required: Although electrotherapy is a safe method, problems such as skin irritation or overstimulation may occur if the correct electrode placement and current intensity are not adjusted. It is recommended to be applied under the supervision of a physiotherapist or specialist.
- Caution with the pacemaker: For patients with pacemakers, subcutaneous defibrillators or similar electronic devices, electrotherapy may be contraindicated or should be performed with extreme caution.
- Open Wounds and Skin Problems: Electrodes should not be placed directly into open wounds or severe skin lesions.
- Pregnancy and other conditions: In pregnancy, it is important to obtain a doctor's approval, especially with regard to application to the abdomen. Individuals with epilepsy or certain neurological diseases should also be subject to special consideration.
Summary and Conclusion
Electrotherapy offers an effective and safe option for relieving pain, strengthening muscles and accelerating tissue healing. It is used in many musculoskeletal problems and pain syndromes thanks to different current and device combinations. However, as with any treatment method, electrotherapy should be applied under expert supervision, customised according to the needs of the person.
If you are experiencing problems such as muscle or joint pain, injuries or nerve compression, you can discuss with your physiotherapist whether electrotherapy is a suitable option for you. A carefully planned and monitored electrotherapy process can improve your quality of life and help you to perform your daily activities more comfortably.
Our treatments
- Home
- Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
- Electrotherapy